Understand Milialar Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Milialar Disease, a rare genetic disorder also known as Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH), is a condition that affects a small number of individuals worldwide. Despite its obscurity, it’s essential to shed light on this disease to provide information about its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and ongoing clinical trials. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into understanding Milialar Disease and how it can impact those who have it.
What is Milialar Disease?
Milialar Disease is a genetic disorder that impacts the body’s ability to remove cholesterol effectively from the bloodstream. Cholesterol is vital for the body, but when levels become too high, it can lead to serious health issues, such as heart disease and stroke.
In individuals with Milialar Disease, a specific gene mutation hinders the liver from efficiently removing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, commonly known as “bad” cholesterol. Consequently, LDL accumulates in the bloodstream and forms plaques in artery walls.
The severity of Milialar Disease varies depending on whether an individual inherits one or two copies of the mutated gene. Unfortunately, many people with this condition are unaware of it until they experience symptoms or complications related to high cholesterol levels. Regular screenings and genetic testing can help identify the disorder early on and allow for appropriate management strategies.
Causes of Miliary Disease
Milialar disease can have various underlying causes, with mycobacterial infection being the most common. Mycobacteria, including the species responsible for tuberculosis and leprosy, can spread through the bloodstream, leading to Milialar tuberculosis. Other notable causes include:
- Metastatic Cancer: The spread of cancer cells from the primary tumor to distant organs is known as metastatic cancer. This process can result in Milialar disease as cancer cells infiltrate multiple body systems.
- Sarcoidosis: An inflammatory disease affecting diverse organs, sarcoidosis can contribute to the development of Milialar disease.
- Fungal Infections: Conditions such as histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis, caused by fungi, can lead to Milialar disease, often affecting the lungs.
- Silicosis: Exposure to silica dust, commonly found in certain occupational settings, can lead to lung disease and, in some cases, Milialar disease.
Symptoms of Milialar Disease
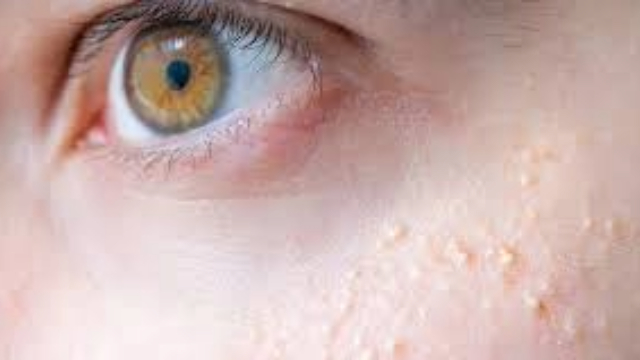
Symptoms of Milialar Disease can vary widely depending on the specific type and severity of the condition. However, some common symptoms include the development of small, raised bumps or lesions on the skin, known as milia. These bumps are typically white or yellowish and are often found on the face, especially around the eyes and cheeks.
Additionally, individuals with Milialar Disease may experience dryness and roughness of the skin, leading to discomfort and itching. In some cases, the disease can affect other organs or systems, causing issues such as blurred vision, sensitivity to light, coughing, and shortness of breath. Early detection and intervention play a vital role in effectively managing symptoms.
Treatment Options for Milialar Disease
- Tailored Treatment Plans: Individualized approaches are crucial, considering the unique nature of each case.
- Medications: Commonly prescribed drugs include immunosuppressants and anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in affected areas.
- Physical Therapy: Beneficial for maintaining muscle strength and flexibility, aiding in symptom management.
- Occupational Therapy: Helps individuals with daily living activities, enhancing their quality of life.
- Surgery: Considered in severe cases when conservative treatments are ineffective. It may involve tissue repair or joint replacement.
- Complementary Therapies: Techniques such as acupuncture or massage therapy can provide symptom relief under healthcare professional guidance.
- Ongoing Management: Since there is no cure for Milialar Disease, continual monitoring and management are essential.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Scheduled check-ups allow healthcare providers to assess disease progression and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Clinical Trials for Milialar Disease
Clinical trials play a crucial role in advancing research and treatment options for rare diseases like Milialar Disease. These trials provide patients with access to innovative therapies that are not yet widely available, contributing directly to scientific progress.
Participating in a clinical trial offers advantages such as close monitoring by a specialized healthcare team and access to potentially groundbreaking therapies. However, participation is entirely voluntary and requires careful consideration of potential risks and benefits.
Interested individuals can explore clinical trial options by consulting their healthcare provider or research organizations specializing in rare diseases. These trials represent hope for improved treatments and, ultimately, finding a cure for Milialar Disease.
Conclusion
Milialar Disease, though rare and challenging to diagnose and manage, can significantly impact individuals worldwide. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for improving the quality of life for those affected.
While the exact cause of Milialar Disease remains elusive, ongoing research continues to unravel its complexities. Genetic mutations and environmental factors likely contribute to its development, necessitating a multidimensional approach to understanding and managing the condition.





